
Understanding Security in Azure: Encryption and Hashing
In this new chapter on basic security concepts, we’re going to look at two key mechanisms: Encryption and Hashing.
Encryption
Encryption is a process used to prevent data from being read or used. To make the data usable again, it must be decrypted using a key. This key may or may not be the same one used to encrypt the data. When the same key is used, the encryption is symmetric; when different keys are used, it’s asymmetric. In asymmetric encryption, the public key is derived from the private key — meaning each private key has a unique public counterpart. A common example of asymmetric encryption is the public/private key system used for managing blockchain accounts.
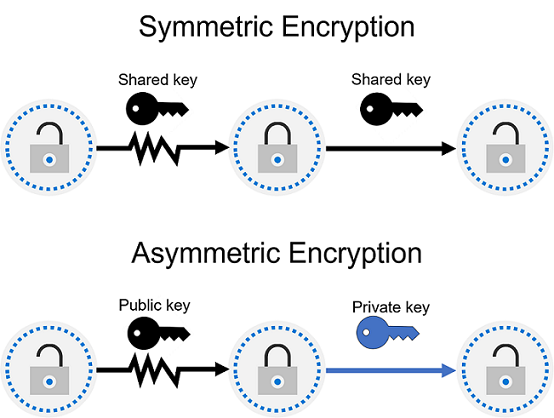
Encryption can be applied to data that’s already stored on a medium like a hard drive, as well as to data that is actively in use or being transmitted from one point to another.
Hashing
Hashing is an algorithm (or function, in programming terms) that takes an input (e.g., a text string) and produces a fixed-size output. In other words, no matter how large the input is, the output is always the same size. Since it’s deterministic, the same input always produces the same output. It’s also irreversible, meaning there’s no way to decode the original input from the output. On top of that, hashing is very fast, which makes it useful as a validation mechanism in technologies like blockchain.

Do you know other uses for encryption and hashing? Share them in the comments. See you in the next entry, where we’ll talk about Governance, Risk, and Compliance.